缘来缘起
core的最原始含意是磁芯,是一种储存设备,dump的意思是倒出,这么coredump的涵义就是:当进程发生异常时,会把当时的显存信息倾倒下来,产生core文件。
每位做linuxC++开发的人,必然会碰到过coredump问题。在C++相关的笔试中,coredump的调试,几乎是一个必考的考点,借以检验应聘者的实战调试经验。
我晓得的一个真实案例是:笔试官让应聘者现场写出一个coredump程序linux 命令,结果应聘者很懵圈,不晓得如何写。这说明,应聘者没有相关的调试经历,何谈通过笔试?
接出来,我们以一个简单的coredump程序为例,来谈谈调试coredump的六种经验和技巧,希望能对你们的开发实战有所帮助,顺便地,横扫这些简单的笔试题。
本文示例的coredump程序如下:
#include
void swap(int *px, int *py)
{
int tmp = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = tmp;
}
int main()
{
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = a + b;
printf("%d, %d, %dn", a, b, c);
swap(&a,& b);
printf("%d, %d, %dn", a, b, c);
int *p = NULL;
*p = 0;
return 0;
}
方式一:代码review
代码review,是一种比较原始的笨方式。对于简单的代码而言,还可以进行review,并且,一旦代码达到数万行,出现coredump后,便无从看起。所以,这些方式很鸡肋,几乎没哪些用。
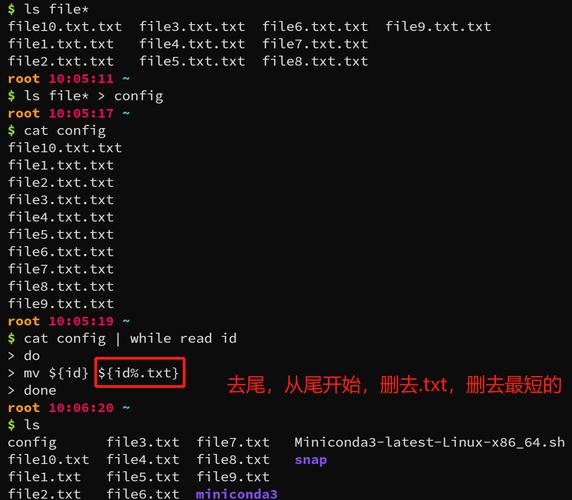
方式二:复印log夹逼
复印log来夹逼,也是一种很简单的方式,在好多场景下,十分奏效。许多学院生和职场菜鸟,容易出现coredump问题,这么,我建议直接用log夹逼。有点类似二分查找,且看具体的坐姿:
#include
void swap(int *px, int *py)
{
int tmp = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = tmp;
}
int main()
{ printf("xxx1n");
int a = 1; printf("xxx2n");
int b = 2; printf("xxx3n");
int c = a + b; printf("xxx4n");
printf("%d, %d, %dn", a, b, c); printf("xxx5n");
swap(&a,& b); printf("xxx6n");
printf("%d, %d, %dn", a, b, c); printf("xxx7n");
int *p = NULL; printf("xxx8n");
*p = 0; printf("xxx9n");
printf("xxx10n");
return 0;
}
编译运行一下:
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ g++ -g test.cpp
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ ./a.out
xxx1
xxx2
xxx3
xxx4
1, 2, 3
xxx5
xxx6
2, 1, 3
xxx7
xxx8
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$
很其实,有xxx8,但没有xxx9linux 不生成core文件,所以linux命令ls,必然是第21行出了问题。
方式三:dmesg+addr2line
有时侯,假如coredump的开关没有打开,难以生成core文件,那如何办呢?也是有办法的!用dmesg和addr2line吧。关于这两个命令的介绍,直接man一下即可。且看具体调试:
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ g++ -g test.cpp
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ ./a.out
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ dmesg
a.out[3709]: segfault at 0 ip 080483c9 sp bff75a60 error 6 in a.out[8048000+1000]
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ addr2line -e a.out 080483c9
/home/ubuntu/test.cpp:21
很其实,代码的第21行出了问题。
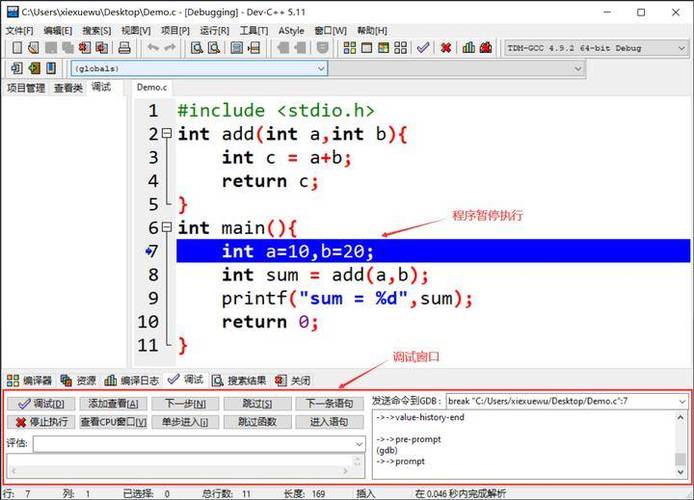
方式四:strace+addr2line
接出来,我们介绍一个重要的linux命令,即strace,直接man一下就晓得,它是用查看系统调用的,我们不过多赘言。来看具体的调试过程:
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ g++ -g test.cpp
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ strace -i ./a.out
[00ff4424] execve("./a.out", ["./a.out"], [/* 22 vars */]) = 0
[0086e2fd] brk(0) = 0x818e000
[0086f6d3] mmap2(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0xb771c000
[0086f5d1] access("/etc/ld.so.preload", R_OK) = -1 ENOENT (No such file or directory)
[0086f494] open("/etc/ld.so.cache", O_RDONLY) = 3
[0086f45e] fstat64(3, {st_mode=S_IFREG|0644, st_size=49072, ...}) = 0
[0086f6d3] mmap2(NULL, 49072, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, 3, 0) = 0xb7710000
[0086f4cd] close(3) = 0
[0086f494] open("/lib/libc.so.6", O_RDONLY) = 3
[0086f514] read(3, "177ELF1113331 N211004"..., 512) = 512
[0086f45e] fstat64(3, {st_mode=S_IFREG|0755, st_size=1855584, ...}) = 0
[0086f6d3] mmap2(0x87e000, 1620360, PROT_READ|PROT_EXEC, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_DENYWRITE, 3, 0) = 0x87e000
[0086f754] mprotect(0xa03000, 4096, PROT_NONE) = 0
[0086f6d3] mmap2(0xa04000, 12288, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_FIXED|MAP_DENYWRITE, 3, 0x185) = 0xa04000
[0086f6d3] mmap2(0xa07000, 10632, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_FIXED|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0xa07000
[0086f4cd] close(3) = 0
[0086f6d3] mmap2(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0xb770f000
[0085a552] set_thread_area({entry_number:-1 -> 6, base_addr:0xb770f6c0, limit:1048575, seg_32bit:1, contents:0, read_exec_only:0, limit_in_pages:1, seg_not_present:0, useable:1}) = 0
[0086f754] mprotect(0xa04000, 8192, PROT_READ) = 0
[0086f754] mprotect(0x876000, 4096, PROT_READ) = 0
[0086f711] munmap(0xb7710000, 49072) = 0
[00ba1424] fstat64(1, {st_mode=S_IFCHR|0620, st_rdev=makedev(136, 1), ...}) = 0
[00ba1424] mmap2(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0xb771b000
[00ba1424] write(1, "1, 2, 3n", 81, 2, 3
) = 8
[00ba1424] write(1, "2, 1, 3n", 82, 1, 3
) = 8
[08048479] --- SIGSEGV (Segmentation fault) @ 0 (0) ---
[????????] +++ killed by SIGSEGV (core dumped) +++
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ addr2line -e a.out 08048479
/home/ubuntu/test.cpp:21
很其实,代码的第21行出了问题。
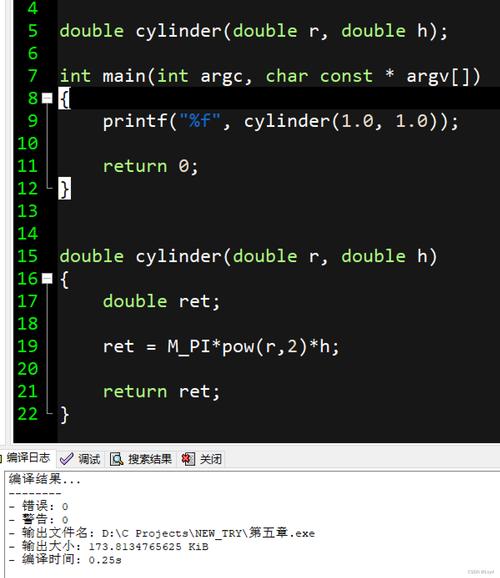
方式五:valgrind
之前,在调试显存泄露时,介绍过valgrind,虽然valgrind能查其他更多显存问题,十分强悍。下边,我们来瞧瞧valgrind查coredump问题,如下:
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ g++ -g test.cpp
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ valgrind -v ./a.out
==23889== Memcheck, a memory error detector
==23889== Copyright (C) 2002-2015, and GNU GPL'd, by Julian Seward et al.
==23889== Using Valgrind-3.11.0 and LibVEX; rerun with -h for copyright info
==23889== Command: ./a.out
......(部分非关键信息,我省略了哈)
==23889== Invalid write of size 4
==23889== at 0x4006D6: main (test.cpp:21)
==23889== Address 0x0 is not stack'd, malloc'd or (recently) free'd
==23889==
==23889==
==23889== Process terminating with default action of signal 11 (SIGSEGV)
==23889== Access not within mapped region at address 0x0
==23889== at 0x4006D6: main (test.cpp:21)
==23889== If you believe this happened as a result of a stack
==23889== overflow in your program's main thread (unlikely but
==23889== possible), you can try to increase the size of the
==23889== main thread stack using the --main-stacksize= flag.
==23889== The main thread stack size used in this run was 8388608.
--23889-- REDIR: 0x4ebe4f0 (libc.so.6:free) redirected to 0x4c2ed80 (free)
==23889==
==23889== HEAP SUMMARY:
==23889== in use at exit: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==23889== total heap usage: 1 allocs, 1 frees, 1,024 bytes allocated
==23889==
==23889== All heap blocks were freed -- no leaks are possible
==23889==
==23889== ERROR SUMMARY: 1 errors from 1 contexts (suppressed: 0 from 0)
==23889==
==23889== 1 errors in context 1 of 1:
==23889== Invalid write of size 4
==23889== at 0x4006D6: main (test.cpp:21)
==23889== Address 0x0 is not stack'd, malloc'd or (recently) free'd
==23889==
==23889== ERROR SUMMARY: 1 errors from 1 contexts (suppressed: 0 from 0)
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$
很其实,我们可以见到,第21行有问题,进程在21行coredump了。
方式六:gdb
gdb调试,是本文的重头戏linux 不生成core文件,也几乎是面试笔试的必考内容。话不多说,直接来看坐姿。使用gdba.outcore(不会重新拉取a.out进程)或则gdba.out(会重新拉起a.out进程)都可以,如下:
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ g++ -g test.cpp
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$
ubuntu@VM-0-15-ubuntu:~$ gdb a.out
GNU gdb (Ubuntu 7.11.1-0ubuntu1~16.5) 7.11.1
Copyright (C) 2016 Free Software Foundation, Inc.

License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law. Type "show copying"
and "show warranty" for details.
This GDB was configured as "x86_64-linux-gnu".
Type "show configuration" for configuration details.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
.
Find the GDB manual and other documentation resources online at:
.
For help, type "help".
Type "apropos word" to search for commands related to "word"...
Reading symbols from a.out...done.
(gdb) r
Starting program: /home/ubuntu/a.out
1, 2, 3
2, 1, 3
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x0000000000400646 in main () at test.cpp:21
21 *p = 0;
(gdb) bt
#0 0x0000000000400646 in main () at test.cpp:21
其实,程序在第21行coredump了。gdb的调试,尤为重要,必须把握。
最后的话
方式千万条,搞定问题第一条。在后续文章中,我们会更多地介绍各类调试方式和方法,快速查杀bug,这样你们就可以少加班啦。祝顺利。
明晚(周日)晚19点准时播出!点击阅读原文,预约直播,抽奖的机率更高哦~
☞苹果因不带充电器被罚款200万美元;杨笠代言英特尔被抵制,品牌方连夜下架;Linux考虑加入对Rust的支持 | 极客头条☞Flutter 即将占领整个 Web 开发☞“Mac 不靠谱”,被苹果放弃的英特尔开启“嘲讽技能”!
☞为什么不能完全相信自动驾驶?
