后面我们介绍到如何编译出内核模块.ko文件,之后还加载了这个驱动模块。并且,那种驱动代码还不健全,驱动写好后如何在应用层使用也没有介绍。
字符设备具象
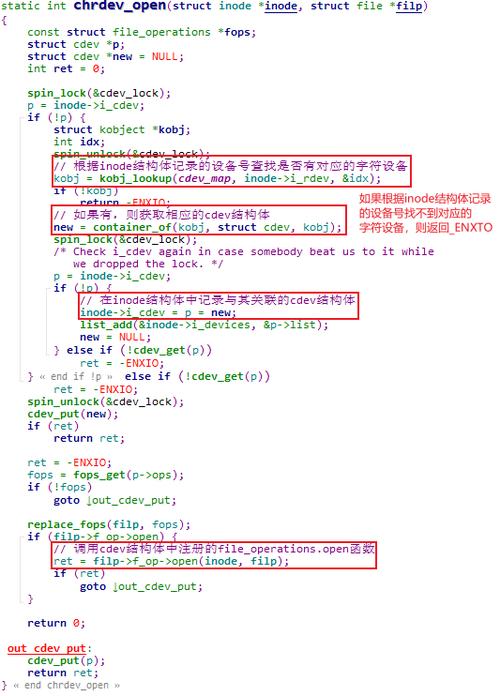
Linux内核上将字符设备具象成一个具体的数据结构(structcdev),我们可以理解为字符设备对象,cdev记录了字符设备的相关信息(设备号、内核对象),字符设备的打开、读写和关掉等操作插口(file_operations),在我们想要添加一个字符设备时,就是将这个对象注册到内核中linux 驱动设备,通过创建一个文件(设备节点)绑定对象的cdev,当我们对这个文件进行读写操作时,就可以通过虚拟文件系统,在内核中找到这个对象及其操作插口,进而控制设备。
在Linux中,我们使用设备编号来表示设备,主设备号分辨设备类别,次设备号标示具体的设备。cdev结构体被内核拿来记录设备号,而在使用设备时,我们一般会打开设备节点,通过设备节点的inode结构体和file结构体最终找到file_operations结构体,并从file_operations结构体中得到操作设备的具体方式。
设备号
Linux根目录下有/dev这个文件夹,专门拿来储存设备中的驱动程序,我们可以使用ls-l以列表的方式列举所有设备。
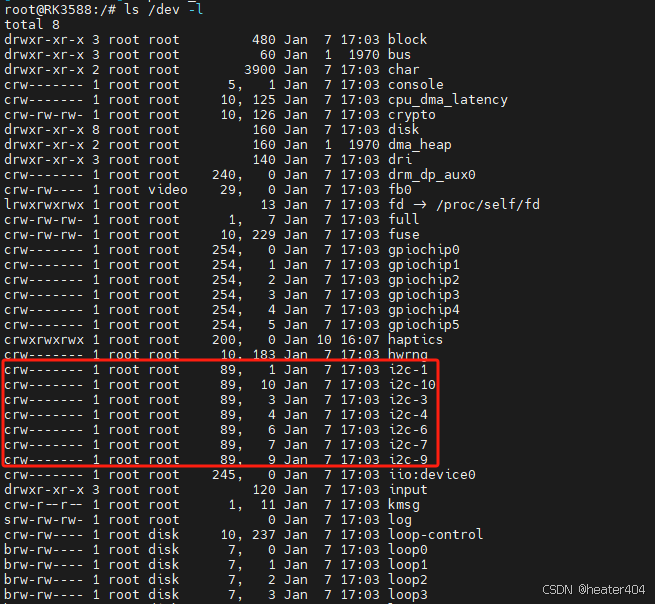
通常来说,主设备号指向设备的驱动程序,次设备号指向某个具体的设备。如上图,i2c-3和i2c-4属于不同设备并且共用一套驱动程序。
typedef u32 __kernel_dev_t;
typedef __kernel_dev_t dev_t;
#define MINORBITS 20
#define MINORMASK ((1U << MINORBITS) - 1)
#define MAJOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) >> MINORBITS))
#define MINOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) & MINORMASK))
#define MKDEV(ma,mi) (((ma) << MINORBITS) | (mi))
在内核中,dev_t拿来表示设备编号,dev_t是一个32位的数,其中,高12位表示主设备号,低20位表示次设备号。也就是理论上主设备号取值范围:0-2^12,次设备号0-2^20。
在kdev_t中linux 驱动设备,设备编号通过移位操作最终得到主/次设备号码,同样主/次设备号也可以通过位运算弄成dev_t类型的设备编号,具体实现参看下边代码MAJOR(dev)、MINOR(dev)和MKDEV(ma,mi)。
cdev结构体
内核通过一个散列表来记录设备编号。
struct cdev {
struct kobject kobj;
struct module *owner;
const struct file_operations *ops;
struct list_head list;
dev_t dev;
unsigned int count;
} __randomize_layout;
设备节点
设备节点是啥呢,似乎就是设备文件。设备节点被创建在/dev目录下,是联接内核与用户层的枢纽。
加载了设备驱动后,我们可以通过mknod命令来自动创建设备节点,也可以通过代码实现手动创建设备节点。
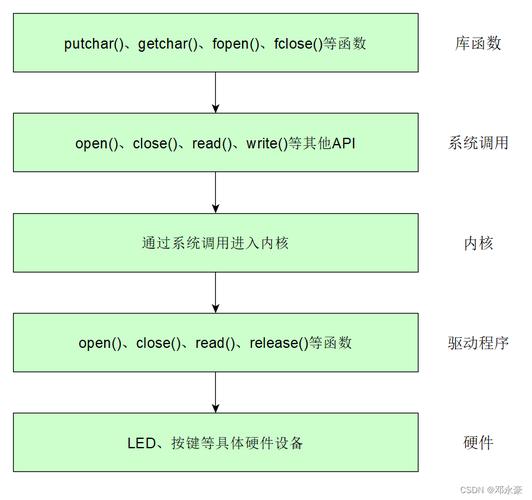
应用程序通过一组标准化的调用执行访问设备linux命令chm,这种调用独立于任何特征的驱动程序。而驱动程序负责将这种标准调用映射到实际硬件的特有操作。
数据结构
在驱动开发过程中,不可防止要涉及到三个重要的内核数据结构。
file_operations结构体
file_operations就是把系统调用和驱动程序关联上去的关键数据结构。以下代码中只列举本章使用到的部份函数。
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *)
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
};
在使用read和write函数时,须要使用copy_to_user函数以及copy_from_user函数来进行数据访问,写入/读取成功函数返回0,失败则会返回未被拷贝的字节数。
static inline long copy_from_user(void *to, const void __user * from, unsigned long n)
static inline long copy_to_user(void __user *to, const void *from, unsigned long n)
file结构体
内核中用file结构体来表示每位打开的文件,每打开一个文件,内核会创建一个结构体,并将对该文件上的操作函数传递给该结构体的成员变量f_op,当文件所有实例被关掉后,内核会释放这个结构体。如下代码中,只列举了我们本章须要了解的成员变量。
struct file {
{......}
const struct file_operations *f_op;
/* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */
void *private_data;
{......}
};
inode结构体
VFSinode包含文件访问权限、属主、组、大小、生成时间、访问时间、最后更改时间等信息。它是Linux管理文件系统的最基本单位,也是文件系统联接任何子目录、文件的桥梁。内核使用inode结构体在内核内部表示一个文件。
inode结构体包含了一大堆文件相关的信息,并且就针对驱动代码来说,我们只要关心其中的两个域即可:
struct inode {
dev_t i_rdev;
{......}
union {
struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe; /* linux内核管道 */
struct block_device *i_bdev; /* 如果这是块设备,则设置并使用 */
struct cdev *i_cdev; /* 如果这是字符设备,则设置并使用 */
char *i_link;
unsigned i_dir_seq;
};
{......}
};
字符设备驱动程序框架
在驱动入口函数中
分配设备号注册字符设备创建设备节点
在驱动出口函数中
删掉字符设备归还设备号删掉设备节点已弃用的注册字符设备函数
static inline int register_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name,const struct file_operations *fops)
static inline void unregister_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name)
这一组函数时Linux版本2.4之前的注册形式,每注册一个字符设备,都都会连续注册0~255个次设备,使她们绑定在同一个file_operationis操作方式结构体上,而我们在大多数情况下,都只会用到很少的次设备号,所以会导致资源的极大浪费。所以如今极少用它。
字符设备号的申请和释放静态申请
register_chrdev_region函数用于静态地为一个字符设备申请一个或多个设备编号
int register_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name)
void unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count)
参数:
返回值:返回0表示申请成功,失败则返回错误码。
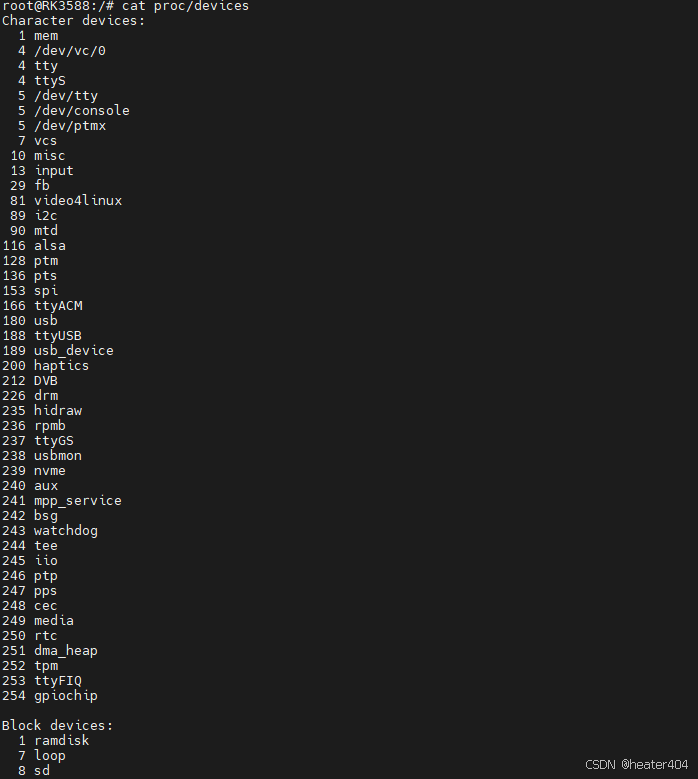
静态申请设备号是我们人为确定好了设备号,再去申请设备号,属于静态申请。可以通过命令cat/proc/devices来查询内核已使用的主设备号。
动态申请
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count, const char *name)
void unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count)
参数:
返回值:返回0表示申请成功,失败则返回错误码
字符设备的注册和注销
后面我们早已提及过了,编撰一个字符设备最重要的事情,就是要实现file_operations这个结构体中的函数。实现以后,怎样将该结构体与我们的字符设备结构体相关联呢?内核提供了cdev_init函数红旗linux安装,来实现这个过程。
void cdev_init(struct cdev *cdev, const struct file_operations *fops)
参数:
返回值:无
cdev_add函数用于向内核的cdev_map散列表添加一个新的字符设备
int cdev_add(struct cdev *p, dev_t dev, unsigned count)
参数:
返回值:错误码
从系统中删掉cdev,cdev设备将难以再打开,但任何早已打开的cdev将保持不变,虽然在cdev_del返回后,它们的FOP依然可以调用。
void cdev_del(struct cdev *p)
参数:
返回值:无
设备节点的创建和销毁
创建类的定义在/linux-4.1.15/include/linux/device.h中。
#define class_create(owner, name)
({
static struct lock_class_key __key;
__class_create(owner, name, &__key);
})
删掉类:
extern void class_destroy(struct class *cls)
struct device *device_create(struct class *class, struct device *parent,
dev_t devt, void *drvdata, const char *fmt, ...)
参数:
返回值:成功时返回structdevice结构体表针,错误时返回ERR_PTR().
删掉使用device_create函数创建的设备
void device_destroy(struct class *class, dev_t devt)
参数:
返回值:无
不仅使用代码创建设备节点,还可以使用mknod命令创建设备节点。
用法:mknod设备名设备类型主设备号次设备号
如:
mknod /dev/haptics c 200 0
这个class和device具体是哪些,我们前面再介绍,目前我们只管这样用就行。
源码
/*
* Silicon Integrated Co., Ltd haptic sih688x haptic driver file
*
* Copyright (c) 2021 kugua
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as published by
* the Free Software Foundation
*/
#include //包含宏定义的头文件
#include //包含初始化加载模块的头文件
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define HAPTICS_DEV_MAJOR 200
#define HAPTICS_DEV_MINOR 0
#define HAPTICS_DEV_NAME "haptics"
#define HAPTICS_DEV_CNT 1
#define HAPTICS_DEV_CLASS_NAME "haptics"
#define HAPTICS_DEV_NODE_NAME "haptics"
#define BUFF_SIZE 128
//数据缓冲区
static char vbuf[BUFF_SIZE]="this is driver";
static dev_t dev_id;//设备号
static struct cdev haptics_dev;//设备
struct class *class;

struct device *device;
static int major = HAPTICS_DEV_MAJOR;//主设备号
static int minor = HAPTICS_DEV_MINOR;//次设备号
//打开设备
static int haptics_open(struct inode* inode,struct file * filp)
{
printk("%sn",__FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}
//关闭设备
static int haptics_release(struct inode* inode ,struct file* filp)
{
printk("%sn",__FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}
//读设备
static ssize_t haptics_read(struct file* filp, char __user *buf,size_t count,loff_t* ppos)
{
unsigned long p = *ppos;
int ret;
int tmp = count ;
if (p >= BUFF_SIZE)
return 0;
if (tmp > BUFF_SIZE - p)
tmp = BUFF_SIZE - p;
ret = copy_to_user(buf, vbuf+p, tmp);
*ppos +=tmp;
return tmp;
}
//写设备
static ssize_t haptics_write(struct file* filp,const char __user *buf,size_t count,loff_t* ppos)
{
unsigned long p = *ppos;
int ret;
int tmp = count ;
if (p > BUFF_SIZE)
return 0;
if (tmp > BUFF_SIZE - p)
tmp = BUFF_SIZE - p;
memset(vbuf,0,BUFF_SIZE);
ret = copy_from_user(vbuf, buf, tmp);
*ppos += tmp;
return tmp;
}
static struct file_operations haptics_fops=
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = haptics_open,
.release = haptics_release,
.read = haptics_read,
.write = haptics_write,
};
static int __init haptics_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
//内核层只能使用printk,不能使用printf
printk(KERN_EMERG "%sn",__FUNCTION__); //输出等级为0
//申请设备号
if(major)
{
dev_id = MKDEV(major,minor);
//静态申请
ret = register_chrdev_region(dev_id, HAPTICS_DEV_CNT, HAPTICS_DEV_NAME);
if(0 == ret)
{
printk("register_chrdev_region ok,major=%d minor=%dn",MAJOR(dev_id),MINOR(dev_id));
}
}
else
{
//动态申请
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev_id, minor, HAPTICS_DEV_CNT, HAPTICS_DEV_NAME);
if(0 == ret)
{
printk("alloc_chrdev_region ok,major=%d minor=%dn",MAJOR(dev_id),MINOR(dev_id));
}
}
//注册字符设备
haptics_dev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&haptics_dev,&haptics_fops);
cdev_add(&haptics_dev,dev_id,HAPTICS_DEV_CNT);
//自动创建设备节点
class = class_create(THIS_MODULE,HAPTICS_DEV_CLASS_NAME);
device = device_create(class,NULL,dev_id,NULL,HAPTICS_DEV_NODE_NAME);
return 0;
}
static void __exit haptics_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_EMERG "%sn",__FUNCTION__); //输出等级为0
//释放设备号
unregister_chrdev_region(dev_id,HAPTICS_DEV_CNT);
//注销字符设备
cdev_del(&haptics_dev);
//删除设备节点
device_destroy(class,dev_id);
class_destroy(class);
}
module_init(haptics_init);//驱动入口
module_exit(haptics_exit);//驱动出口
MODULE_AUTHOR("");//声明作者信息
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Haptic Driver V1.0.0"); //对这个模块作一个简单的描述
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");//声明开源许可证
// "GPL" 是指明 这是GNU General Public License的任意版本
// “GPL v2” 是指明 这仅声明为GPL的第二版本
还有应用层代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/*
argc:应用程序参数个数,包括应用程序本身
argv[]:具体的参数内容,字符串形式
./main r表示读 w表示写
*/
int main(int argc,char * argv[])
{
char *wbuf = "Hello Worldn";
char rbuf[128];
char* filename;
int fd=0;
if(argc!=3)
{
printf("error usagen");
return -1;
}
filename=argv[1];
fd = open(filename,O_RDWR);
if(fd<0)
{
printf("can not open file %sn",filename);
return -2;
}
if(0 == strcmp(argv[2],"r"))
{
read(fd, rbuf, 128);
//打印读取的内容
printf("The content : %sn", rbuf);
}else if(0 == strcmp(argv[2],"w"))
{
write(fd, wbuf, strlen(wbuf));
}else
{
printf("error usagen");
}
close(fd);
}
root@RK3588:/# insmod haptics.ko
[ 53.773224] haptics_init
[ 53.773264] register_chrdev_region ok,major=200 minor=0
root@RK3588:/# ./main /dev/haptics w
[ 56.270812] haptics_open
[ 56.270867] haptics_release
root@RK3588:/# ./main /dev/haptics r
[ 59.249993] haptics_open
The content : Hello World
[ 59.250155] haptics_release
root@RK3588:/#
优化源码
对于上述驱动代码,有几点须要优化
class名称、node名称通常与驱动名称一致我们定义了好多全局变量,虽然我们可以具象出一个设备结构体,这个结构体去包含这些成员变量一套驱动代码,是须要兼容多个设备的,所以应当尽量少用全局变量,须要思索怎么兼容多设备
/*
* Silicon Integrated Co., Ltd haptic sih688x haptic driver file
*
* Copyright (c) 2021 heater
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as published by
* the Free Software Foundation
*/
#include //包含宏定义的头文件
#include //包含初始化加载模块的头文件
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define HAPTICS_CDEV_MAJOR 200
#define HAPTICS_CDEV_MINOR 0
#define HAPTICS_CDEV_NAME "haptics"
#define HAPTICS_CDEV_CNT 1
#define BUFF_SIZE 128
struct haptics_dev
{
struct cdev haptics_cdev;//字符设备
dev_t dev_id;//设备号
struct class *class; //类
struct device *device; //设备
int major;//主设备号
int minor;//次设备号
char vbuf[BUFF_SIZE];//数据缓冲区
};
struct haptics_dev mdev;//定义一个设备结构体
//打开设备
static int haptics_open(struct inode* inode,struct file * filp)
{
printk("%sn",__FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}
//关闭设备
static int haptics_release(struct inode* inode ,struct file* filp)
{
printk("%sn",__FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}
//读设备
static ssize_t haptics_read(struct file* filp, char __user *buf,size_t count,loff_t* ppos)
{
unsigned long p = *ppos;
int ret;
int tmp = count ;
if (p >= BUFF_SIZE)
return 0;
if (tmp > BUFF_SIZE - p)
tmp = BUFF_SIZE - p;
ret = copy_to_user(buf, mdev.vbuf+p, tmp);
*ppos +=tmp;
return tmp;
}
//写设备
static ssize_t haptics_write(struct file* filp,const char __user *buf,size_t count,loff_t* ppos)
{
unsigned long p = *ppos;
int ret;
int tmp = count ;
if (p > BUFF_SIZE)
return 0;
if (tmp > BUFF_SIZE - p)
tmp = BUFF_SIZE - p;
memset(mdev.vbuf,0,BUFF_SIZE);
ret = copy_from_user(mdev.vbuf, buf, tmp);
*ppos += tmp;
return tmp;
}
static struct file_operations haptics_fops=
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = haptics_open,
.release = haptics_release,
.read = haptics_read,
.write = haptics_write,
};
static int __init haptics_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
//内核层只能使用printk,不能使用printf
printk(KERN_EMERG "%sn",__FUNCTION__); //输出等级为0
mdev.major = HAPTICS_CDEV_MAJOR;//预定义的主设备号
mdev.minor = HAPTICS_CDEV_MINOR;//预定义的次设备号
//申请设备号
if(mdev.major)//如果预定义的主设备号不为0,则需要静态申请设备号
{
mdev.dev_id = MKDEV(mdev.major,mdev.minor);
//静态申请
ret = register_chrdev_region(mdev.dev_id, HAPTICS_CDEV_CNT, HAPTICS_CDEV_NAME);
if(0 == ret)
{
printk("register_chrdev_region ok,major=%d minor=%dn",MAJOR(mdev.dev_id),MINOR(mdev.dev_id));
}
}
else//如果预定义的主设备号为0,则需要动态申请设备号
{
//动态申请
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&mdev.dev_id, mdev.minor, HAPTICS_CDEV_CNT, HAPTICS_CDEV_NAME);
if(0 == ret)
{
mdev.major = MAJOR(mdev.dev_id);
mdev.minor = MINOR(mdev.dev_id);
printk("alloc_chrdev_region ok,major=%d minor=%dn",MAJOR(mdev.dev_id),MINOR(mdev.dev_id));
}
}
//注册字符设备
mdev.haptics_cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&mdev.haptics_cdev,&haptics_fops);
cdev_add(&mdev.haptics_cdev,mdev.dev_id,HAPTICS_CDEV_CNT);
//自动创建设备节点
mdev.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE,HAPTICS_CDEV_NAME);
mdev.device = device_create(mdev.class,NULL,mdev.dev_id,NULL,HAPTICS_CDEV_NAME);
return 0;
}
static void __exit haptics_exit(void)
{
//释放设备号
unregister_chrdev_region(mdev.dev_id,HAPTICS_CDEV_CNT);
//注销字符设备
cdev_del(&mdev.haptics_cdev);
//删除设备节点
device_destroy(mdev.class,mdev.dev_id);
class_destroy(mdev.class);
printk(KERN_EMERG "%sn",__FUNCTION__); //输出等级为0
}
module_init(haptics_init);//驱动入口
module_exit(haptics_exit);//驱动出口
MODULE_AUTHOR("");//声明作者信息
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Haptics Driver V1.0.0"); //对这个模块作一个简单的描述
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");//声明开源许可证
// "GPL" 是指明 这是GNU General Public License的任意版本
// “GPL v2” 是指明 这仅声明为GPL的第二版本
